Comprehensive IP Valuation Methods Workshop
Types of Intellectual Property and Their Valuation Methods
Comprehensive IP Valuation Methods Workshop
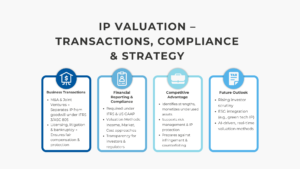
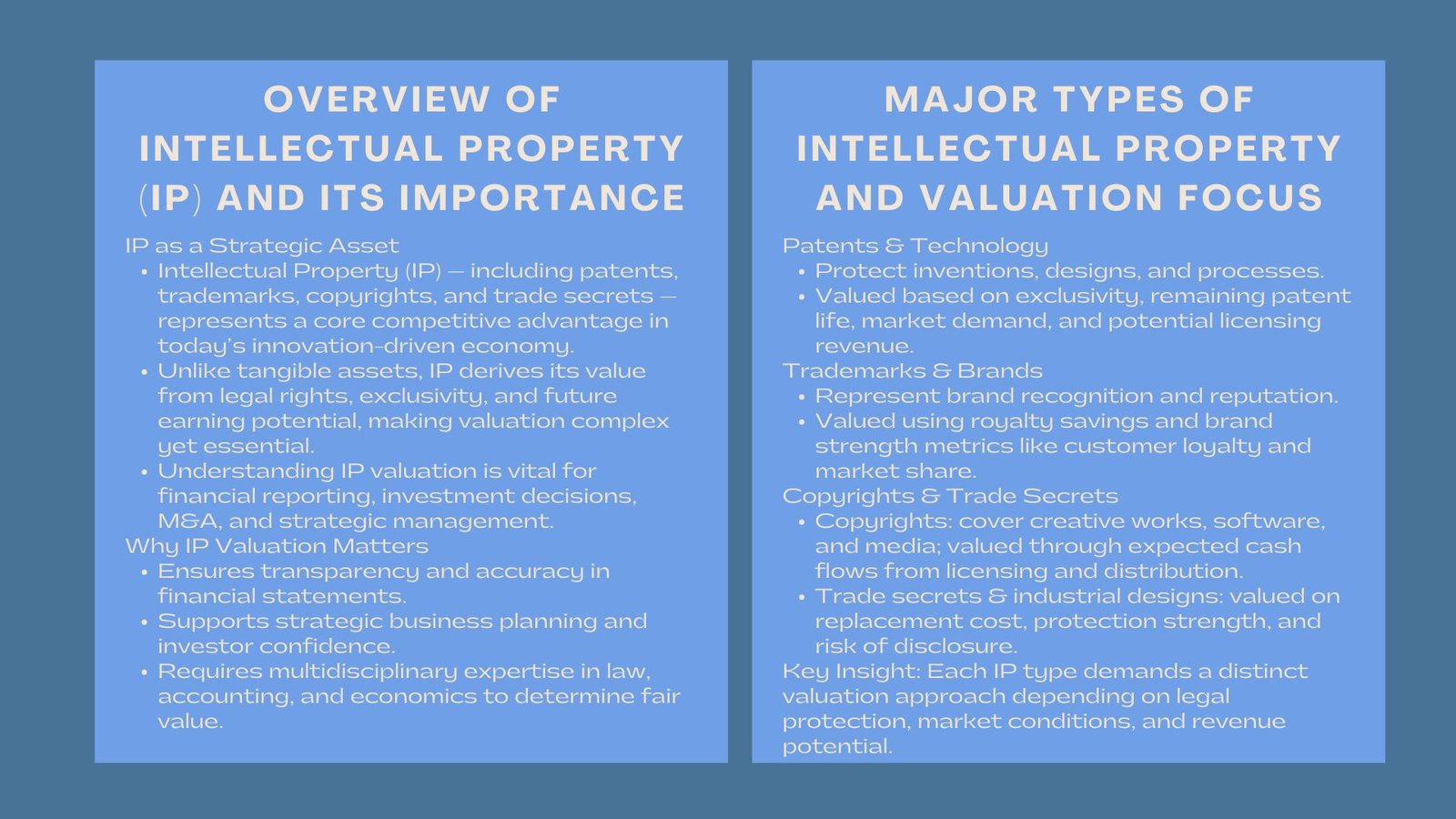
Intellectual property (IP) is a highly potent source of competitive advantage in the modern market characterized by the emphasis on innovation. Intangible assets such as proprietary software, international brand identities, and others can greatly benefit the market location and enterprise worth of a company. It is important to the businesses, investors, and the auditors to understand the various types of IP and their valuation so as to gain transparency in the financial reporting and strategic decision making.
Valuation of IP is a highly complicated yet important procedure. The value of intellectual property cannot be determined by the market prices that are observable in the case of tangible assets, since the value of intellectual property is based on the legal rights, market potential, and future economic advantages. That value would need a professional skill and a good knowledge of accounting economics and law.
Significant Forms of Intellectual Property.
Patents and Technology
Patents secure inventions, technical designs as well as innovative processes which have commercial use. They are usually valued based on exclusivity- the capacity not to allow other people to utilize or copy the identical innovation. Common factors to be taken into consideration during patent valuation include the remaining life of the patent, the state of technology, need in the market and the possible revenue of licensing the patents. In industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics and renewable energy, in many cases the portfolio of patents can constitute a large fraction of overall enterprise value.
Trademarks and Brands
The trademarks protect the brand name of a company, its name, logo, and symbols which are used to identify a product or services. The brand strength can be used to create customer loyalty, high prices, and domination internationally. Trademarks and brands can only be valued when the reputation, perception of the consumers, and competitive positioning of the market are considered. Brand valuation is often based on the sales projections, royalties savings and similar licensing contracts.
Copyrights, Designs, and Trade Secrets.
Copyrights and the Creative Works.
The artistic and literary works that are covered by copyrights include software, music, films, and written works. In the digital economy, copyright commonly relates to media materials and code of software that can be reintroduced to form a stream of recurring revenue. The valuation models on these assets center on anticipated cash flows on licensing, distribution rights or subscription revenues. Other aspects that analysts evaluate include ownership of legal rights, renewals and the commercial viability of future releases.
Trade Secrets and Industrial Designs.
Industrial designs protect the esthetic features of an object, the form, composition, and ornamentation of objects, whereas trade secrets embrace trade secrets, i.e., confidential business information, e.g., formulas, processes, or data sets. They are based on their exclusivity and secrecy capacity. The appraisal of these assets incorporates estimates of the replacement costs, protection and competitive edge of confidentiality. Trade secrets may have their economic value quickly eroded in case they are exposed or copied.
Intellectual Property Valuation Methods in Singapore
Market-Based Valuation
Value is defined through the market-based method, which involves comparing the IP with the similar assets sold or licensed on similar terms. It is best used in cases where there is good market data available like popular trademarks or patented technology with established licensing transactions. In most instances however, it may not be easy to find precise analogies because of confidentiality and the idiosyncrasy of IP assets.
Income-Based Valuation
Income approach uses value which is measured in terms of the present value of the economic benefits of the IP which are generated in the future. Such techniques as the Relief from Royalty Method, which estimates the royalties that are saved by holding the IP, as opposed to licensing it, and the Multi-Period Excess Earnings Method (MPEEM), which separates cash flows caused by solely the IP asset, are part of this method. These approaches form the foundation of intellectual property valuation methods for different asset types, providing robust, data-driven insights into expected financial performance.
Hybrid Approaches and Cost-Based Approaches.
Cost Approach
The cost method establishes value on the cost of recreating or replacing the IP, which includes the cost of developing, testing and legal registration costs. The approach works well in situations where the market or income information is not available, e.g., in the case of early stage studies or commercially developed software. Nevertheless, it might not be a complete usage of the commercial potential or competitive advantage offered by the asset.
Hybrid and Professional Approaches.
Practically, valuers tend to blend several techniques in order to have a moderated analysis. An example of this is to take a patent portfolio and assign its value based on income and cost method to demonstrate the technological potential and work done on the portfolio.
These professional IP valuation approaches used by valuers and analysts ensure that the final valuation aligns with industry standards, regulatory requirements, and market realities. Hybrid techniques are particularly useful when valuing diversified IP portfolios or performing purchase price allocations under IFRS.
Conclusion
The modern enterprise value is made of intellectual property, but the valuation of intellectual property is among the most specialized in finance. Patents and trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and so on, each type of assets would need a specific methodology and professional discretion. Using the known methods of valuation and following the rules of professionalism, companies can make sure that their intangible assets are taken into account correctly and used to develop the company in the most effective way. With the world economy still moving towards innovation and digitalization, the art of IP valuation will be one of the indispensable skills of businesses and other financial experts.