Professional Patent Valuation Training for Analysts
Valuation of Patents and Technology Assets
Learn the Professional Patent Valuation Training for Analysts
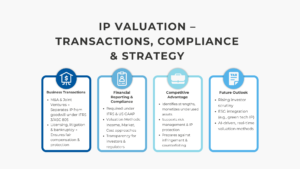
Intellectual property in the form of patents and technology base forms the backbone of the innovative firms. Not only do they safeguard the rights of inventions, but also allow them to license revenues, competitive advantage and attract investments. These assets may constitute over 50% of the market capitalization of a company in other industries, like the pharmaceuticals, semiconductors and software industries. The appreciation of patents should be supported with the systematic knowledge on the legal security, market prospects, and the technical cycle. In addition to compliance, correct valuation leads to decision-making about R & D investment, merger and acquisition, as well as settlement of litigation.
The properly organized PPA is not only offering vividness in terms of the allocation of the purchase price but also acts as a guide on the way forward in terms of the performance in the post-acquisition period. In financial industries where the assets in this model comprise of the customer portfolios, loan repayments, and proprietary platforms are of great constituent in the enterprise value, fair value according to the IFRS 3 requires every element to be of significant relevance to financial reporting and risk management. It also promotes an easier assimilation of systems, accounting structures and compliance processes among merging organizations.
Factors Affecting Patent Valuation
Strength and Enforceability of law:
The range of claims, the life span of the claim and the area covered by jurisdiction has a direct effect on value. Patents that have a global protection or high protection in terms of defense fetch high values. Besides, the enforceability in more than one region which mostly includes key markets like the U.S., EU as well as Asia, greatly increases the commercial appeal of a patent. The investors and acquirers will prefer to invest in an IP portfolio that is characterized by proper ownership documentation and has a good enforcement track record as this will reduce the legal risk and guarantee good future cash flow income.
Technological Obsolescence:
The value of the patents could be destroyed within a short period of time due to the rapid rate of innovation. Technology lifecycle (e.g., software) is shorter, and therefore, can only be sold at a higher discount. On the other hand, long-term or foundation technologies, e.g. pharmaceuticals or industrial apparatuses are subject to such patents, which tend to keep their value long term.
It is important to have knowledge of the level of technology maturity stage hence early technologies could be having a high potential yet with high risks whereas those with a high stability are mature hence are not having an upside. The assessment of obsolescence properly will assist the projection of realistic forecasts in the discounted cash flow models as well as the real valuation of the market longevity.
Commercial Applicability:
The cash flow of a patent and technology asset valuation methods Singapore, which has been created, either by direct product sales or forced licensing, is a fundamental determinant of fair values of the patent. This incorporates the assessment of the technology with respect to its incorporation in business products, scalability, and licensing prospects. An invention that can be used by many industries or can be utilized in flexibility usually attracts a high price.
The other criteria that companies ought to reflect on in estimating the financial return include existing contracts, the opportunities of having a licensee, and the cost of commercialization. Proper valuation will provide effective connections between the technical feasibility and the market readiness so that the IP value should demonstrate the quality of the innovation, as well as, the capacity of the monetization.
Market Requirement and Competition:
Revenue potential is determined by the level of differentiation and entry barriers. A well-built niche market patent can provide results in long-run profitability because of low competition whereas an existing competitive patent may be forced to be price takers. In analysis of the market such as demand trends, the regulatory shifts, and the alternative technologies offer important information on future value. Patents that create or protect market dominance, particularly those that corresponded to the latest megatrends such as the AI, green energy, or bio-technology, were more likely to bring higher strategic value.
To conclude, patent and technology value depends on the convergence of legal strength, business expediency, technological longevity and market applicability. To cater to all these dimensions, a sound valuation framework should be used in order to capture risk and opportunity. These aspects taken in their entirety encourage the companies to protect the integrity of their IP portfolio and also open new avenues that may help them to grow strategically, invest and to maintain a competitive advantage.
Valuation Approaches for Patents
Relief-from-Royalty Method:
The relief-from-royalty method which is the most common method used in valuing patents and technology assets involves the estimation of the value with reference to the hypothetical savings that a firm would incur in terms of the lost royalties in the presence of owning the patent compared to the loss incurred by licensing the patent. To illustrate, in the case where similar technologies are licensed at a 5% rate royalty on sales, the value of the patent will be obtained by determining the present value of such royalty payments avoided upon the remaining economic life of the patent. This strategy is very close to the actual commercial conduct in the real world and indicates the physical advantage of ownership.
The relevance of the royalty rate in this approach is to choose the right royalty rate, how to value intellectual property for M&A and licensing which is either industry-based, licensing databases, or similar transactions; next is the prediction of revenues that can be attributed to the patent; and lastly the selection of a discount rate that has to be applicable to risk. Relief-from-royalty is mainly useful in cases of patents that can be identified in terms of revenue streams and that have high potential of use in the market e.g. branded drugs or fundamental software programs.
Excess Earnings Method:
According to the excess earnings method, part of the overall profits of the business are charged to the patented technology when returns on other contributory assets are made, including working capital, fixed assets and assembled workforce. The profit that the patent produced by its uniqueness is depicted by the residual or the excess earnings. This method will be particularly beneficial when the patent comprises an essential component of a larger product/system that cannot be easily identified and parted with other operating resources.
Practically, the analysts predict the year-end earnings of companies, subtract the mandated returns on the other physical and non-physical assets, and discount the resultant proportion to have the present value. This approach takes into consideration keen judgment in the process of isolating the effect of the patent, although it offers strong indication of economic advantage. It is commonly applied in those valuations that encompass multi-technology companies or integrated systems where it becomes difficult to attribute direct income to the approach with a vision of synergies.
Cost and Market Approaches:
All these are used when it is uncertain of future income like early technology, R&D which is uncommercialized or in fields where similar transactions in the market can easily be made. Estimating the value of recreating or replacing the patent is based on the cost approach incorporating R&D expenditure, testing and regulatory approvals adjusted by the obsolescence and economic utility. It is very appropriate in determining the minimum threshold value of an innovation but can be under-valuing technology with high commercial potential.
Market approach, however, is based on similar transactions, like licensing, royalty or patent sales that are used to estimate fair value. Using the current market statistics, the appraisers can forecast implied valuation multiples or royalty rates that can be used on the subject patent. This approach is especially applicable when a strong set of industry standards is being used, which is the case with consumer electronics or biotechnology industries.
To conclude, there is no universal best valuation method and in fact the most precise ones might be reached as a result of triangulating the various methods. The relief-from-royalty method provides a direct connection with the market behavior, excess earnings method isolates the contribution of intrinsic value and the cost and market methods are the fallback values when there is unpredictability. The integration of these views would enable firms, shareholders, and auditors to have a better, reasonable value of patents and technology that is an accurate description of economic substance and market reality.
Conclusion
Patent valuation is a science and aesthetic process. It considers financial modeling with technical expertise and legal knowledge. A properly reasonable valuation of a patent is capable of serving the purpose of reporting the balance sheet and paying taxes besides providing a strong bargaining power during licensing or acquisition negotiations. The fact that technology is a crucial source of competitiveness in the present world is the point that requires the capacity to measure and manage the value of patents as a strategic necessity of sustainable growth in the business.
Moreover, proper patent valuation increases the transparency levels among investors, auditors and regulators as they may have a clear picture about the way in which intellectual property will add to corporate value. It is also instrumental in strategic choices – both in terms of prioritization of R&D investment to be made, as well as with the process of merger negotiation and raising of capital. Companies with relevant knowledge about their economic potential with regard to their patent portfolio are in a better position to commercialize innovation, protect against infringement and enhance shareholder value.
After all, with further developments in the industrial sector in terms of transforming to a more knowledge based economy, patents have become the core in corporate identity and positioning in the market. The companies which implement strict well-documented valuation activities are adhering to the international standards and are also creating long-term resilience and trust in investors. Here, the value of patents goes beyond accounting, it becomes a foundation of strategic management, planning of innovations and long-lasting value-generation.